5. Standard library of functions: math functions, containers and random numbers#
5.1. Containers#
https://hackingcpp.com/cpp/std/containers.html
5.1.1. Squence containers#

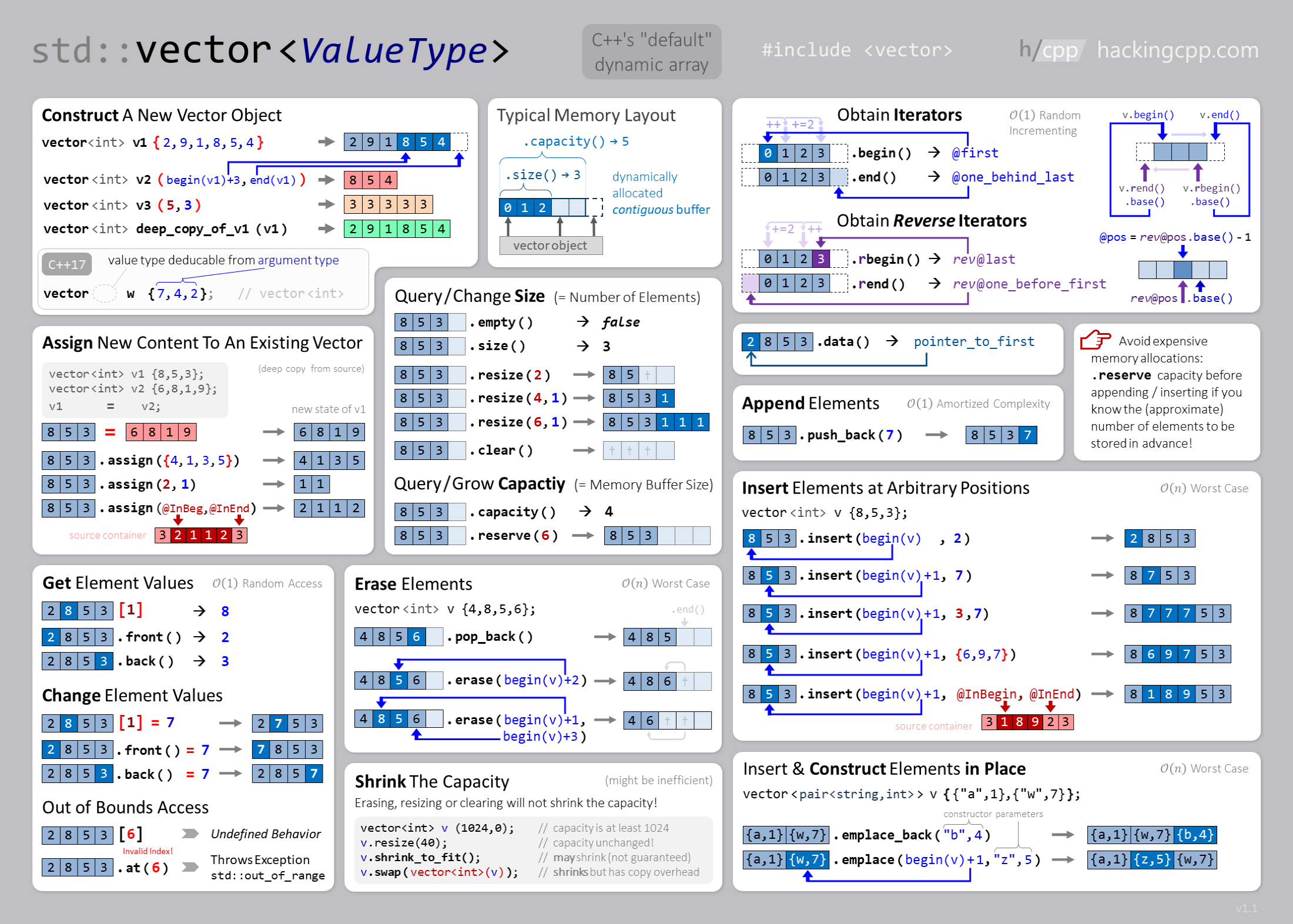
5.1.1.1. Vector#
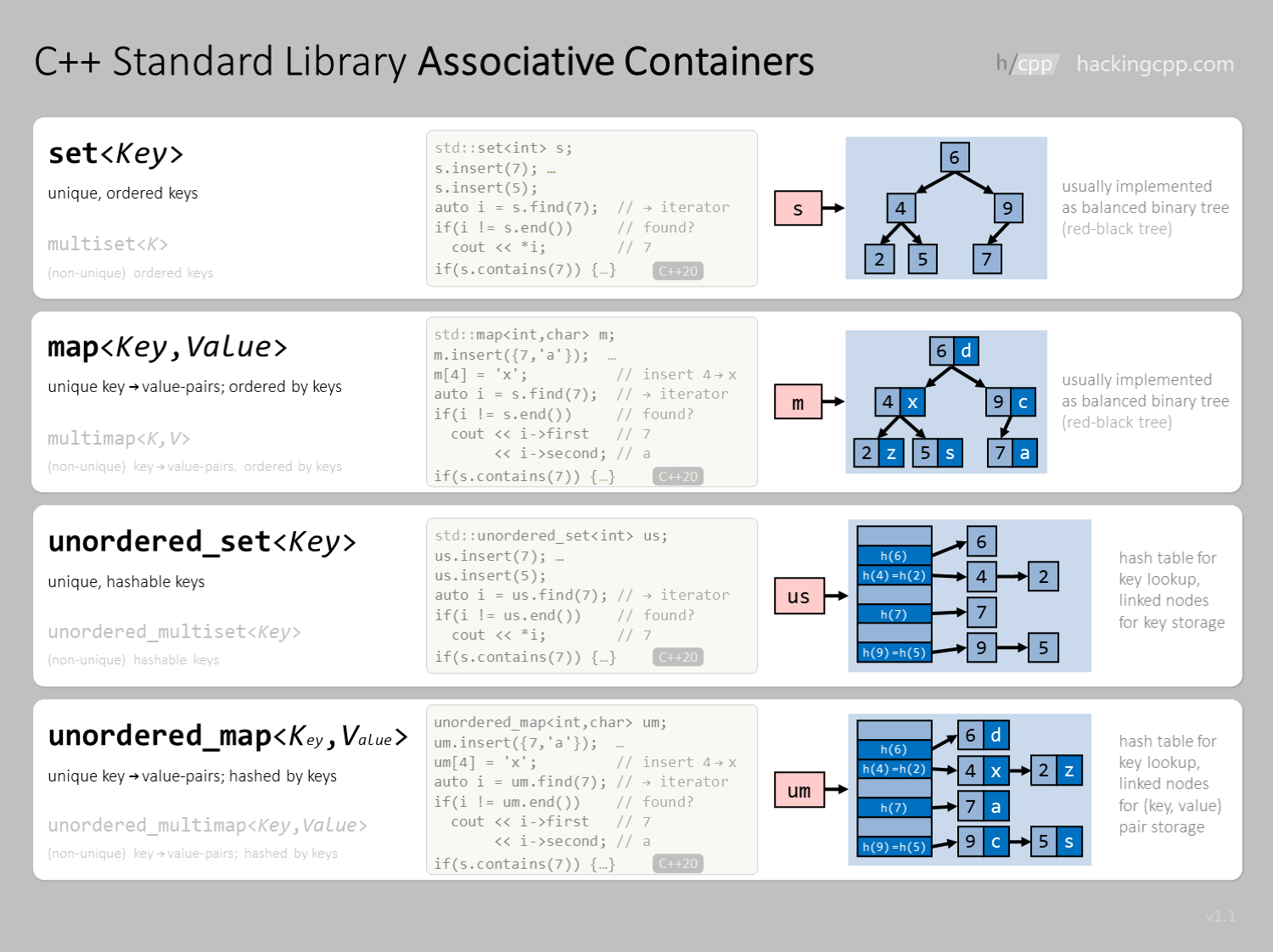
5.1.2. Associative containers#
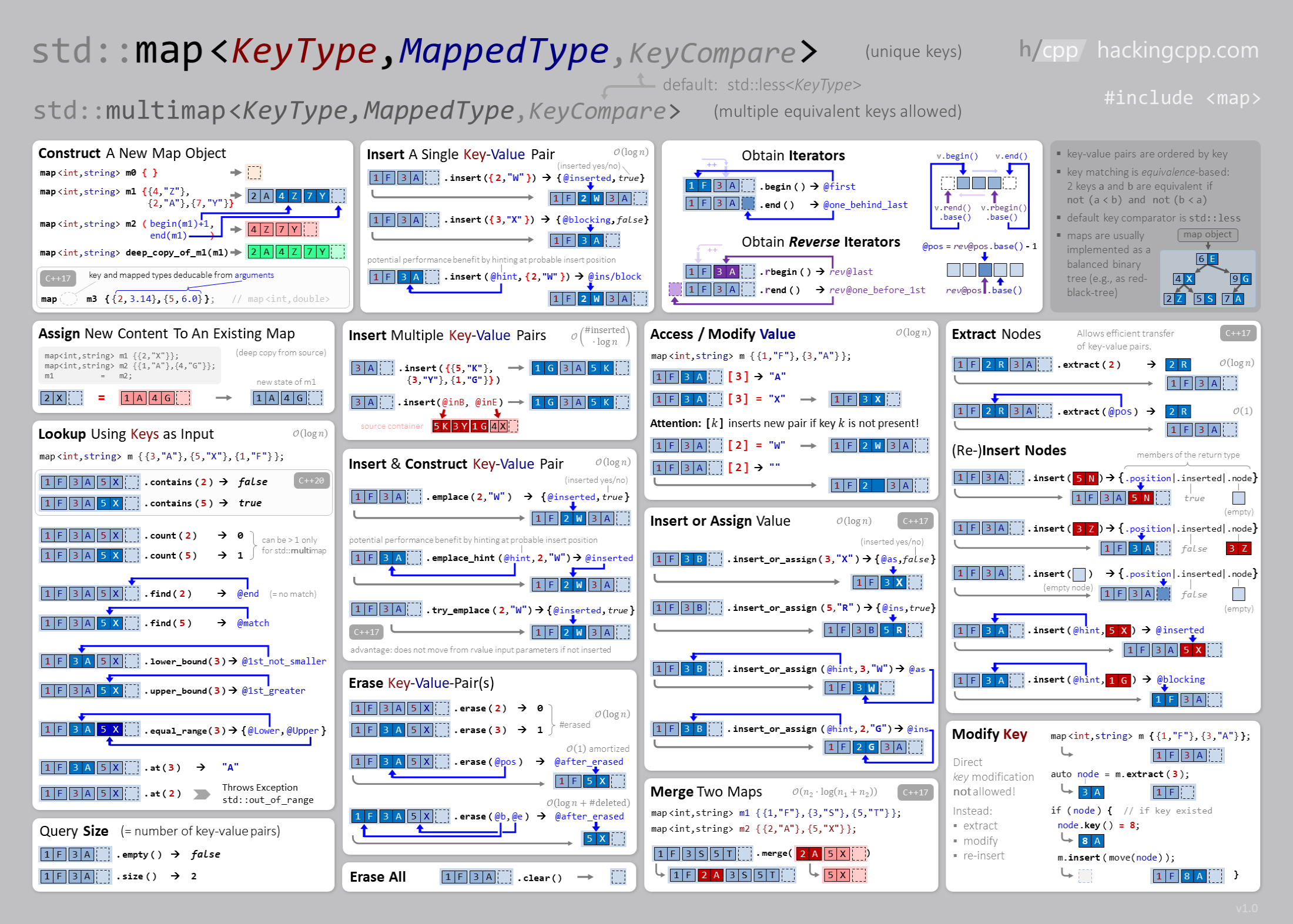
5.1.2.1. Map#
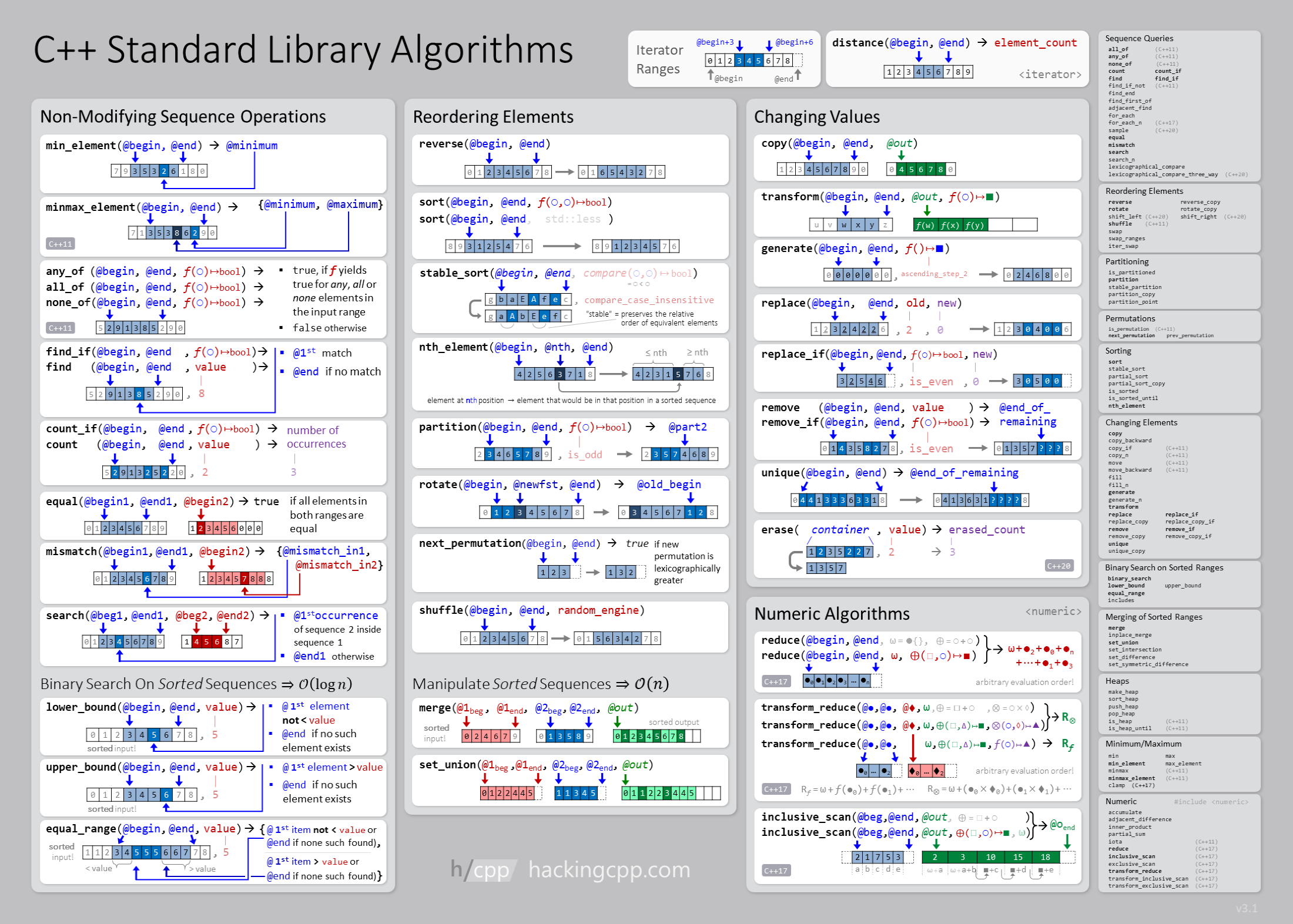
5.2. Algorithms#
5.3. Special functions#
https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/numeric/special_functions
5.3.1. Gamma function#
See http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/numeric/math/tgamma
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
int main(void)
{
const double XMIN = 0.0;
const double XMAX = 11.0;
const double DX = 0.1;
const int NSTEPS = int((XMAX-XMIN)/DX);
for(int ii = 0; ii < NSTEPS; ++ii) {
double x = XMIN + ii*DX;
printf("%25.16e%25.16e\n", x, std::tgamma(x));
}
return 0;
}
5.3.2. Beta function#
// requires c++17
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
int main(void)
{
const double XMIN = -3.0;
const double XMAX = 3.0;
const double YMIN = -3.0;
const double YMAX = 3.0;
const double DELTA = 0.01;
const int NSTEPS = int((XMAX-XMIN)/DELTA);
for(int ii = 0; ii < NSTEPS; ++ii) {
double x = XMIN + ii*DELTA;
for(int jj = 0; jj < NSTEPS; ++jj) {
double y = YMIN + jj*DELTA;
printf("%25.16e%25.16e%25.16e\n", x, y, std::beta(x, y));
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
5.4. Random numbers#
https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/numeric/random
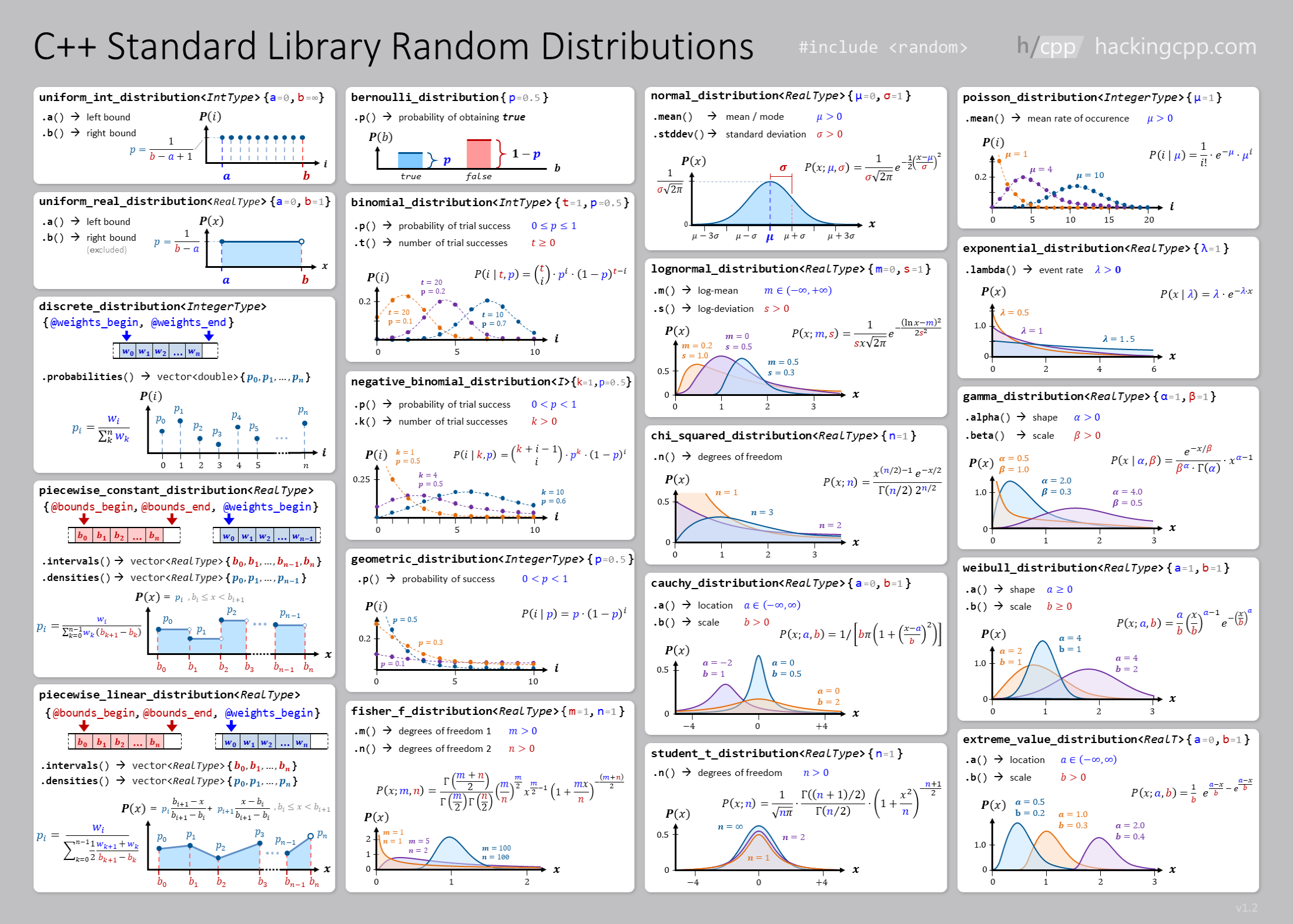
5.4.1. Uniform distribution with random seed#
#include <random>
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
//std::random_device rd; // inicializacion con semilla aleatoria
//std::mt19937 gen(rd()); // genera bits aleatorios
std::mt19937 gen(10);
std::uniform_real_distribution<> dis(1, 2); // distribucion
for(int n = 0; n < 10; ++n) {
std::cout << dis(gen) << std::endl;
}
}
5.4.2. Uniform distribution controlled seed#
#include <random>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int seed = std::atoi(argv[1]);
std::mt19937 gen(seed);
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> dis(1, 2);
for(int n = 0; n < 100000; ++n) {
std::cout << dis(gen) << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
5.4.3. Normal distribution controlled seed#
#include <random>
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
int seed = 1;
std::mt19937 gen(seed);
std::normal_distribution<> dis{1.5, 0.3};
for(int n = 0; n < 100000; ++n) {
std::cout << dis(gen) << std::endl;
}
}
5.4.4. Homework#
Create an histogram to compute the pdf and use it to test the random numbers produced by several distributions.


